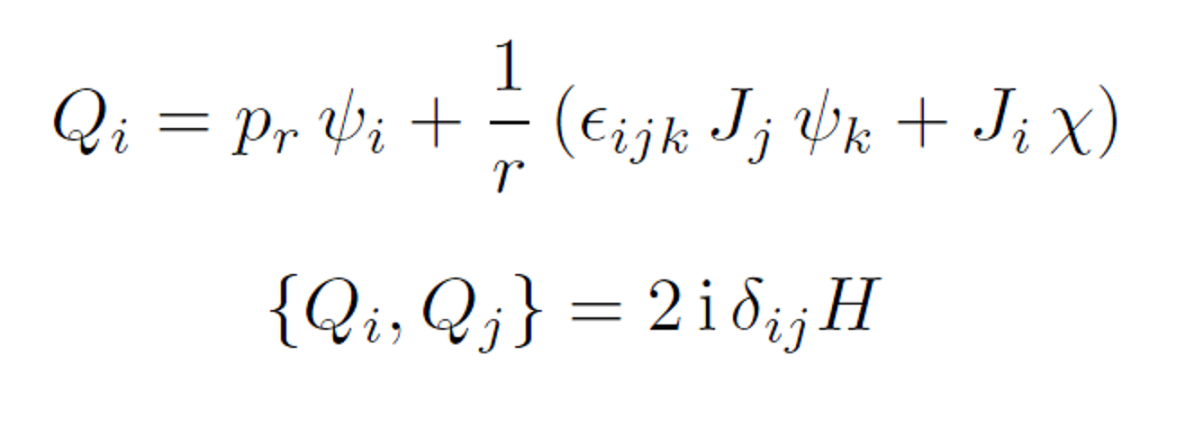We construct superconformal mechanics with N = 3 and N = 4 supersymmetries that were inspired by analogy with the supersymmetric Schwarzian mechanics. The Schwarzian, being another system with superconformal symmetry, provides insight into the field content of supersymmetric mechanics, most notably, on the number and properties of the fermionic fields involved. Adding more fermionic fields (four in the N = 3 case and eight in the N = 4 case) made it possible to construct systems possessing maximal superconformal symmetries in N = 3 and N = 4, namely osp(3|2) and D(1, 2; α). In the case of N = 4 supersymmetry, we explicitly construct a new variant of N = 4 superconformal mechanics in which all bosonic subalgebras of the D(1, 2; α) superalgebra have a bosonic realization. In addition, the constructed systems involve the so(3) currents whose parameterization is not fixed, which allows one to consider different underlying geometries.