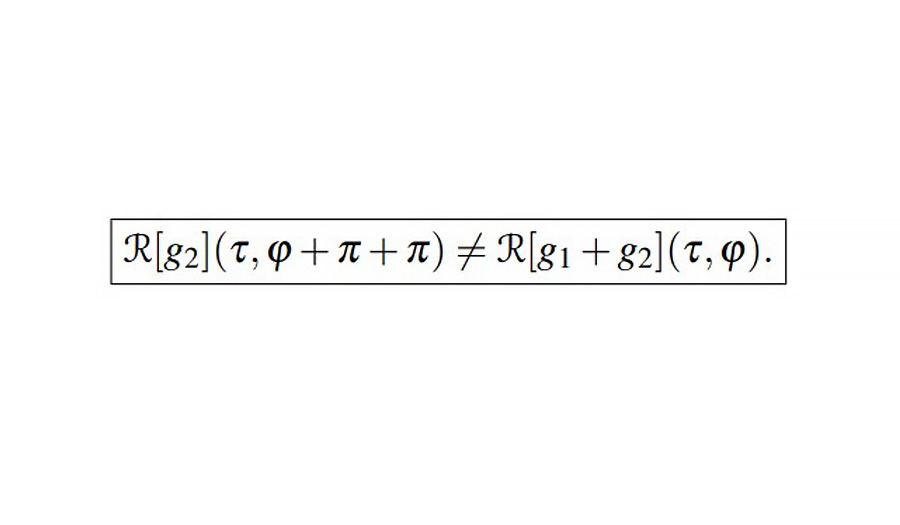The Natural Science Review electronic journal has been published since 2024 according to the decision of the session of the Committee of Plenipotentiaries of the Governments of the JINR Member States dated 24.03.2024. The international intergovernmental organization Joint Institute for Nuclear Research is the journal’s founder and publisher.
Natural Science Review is an international online peer–reviewed periodical scientific journal on natural and technical sciences.
Open issue October — December 2025
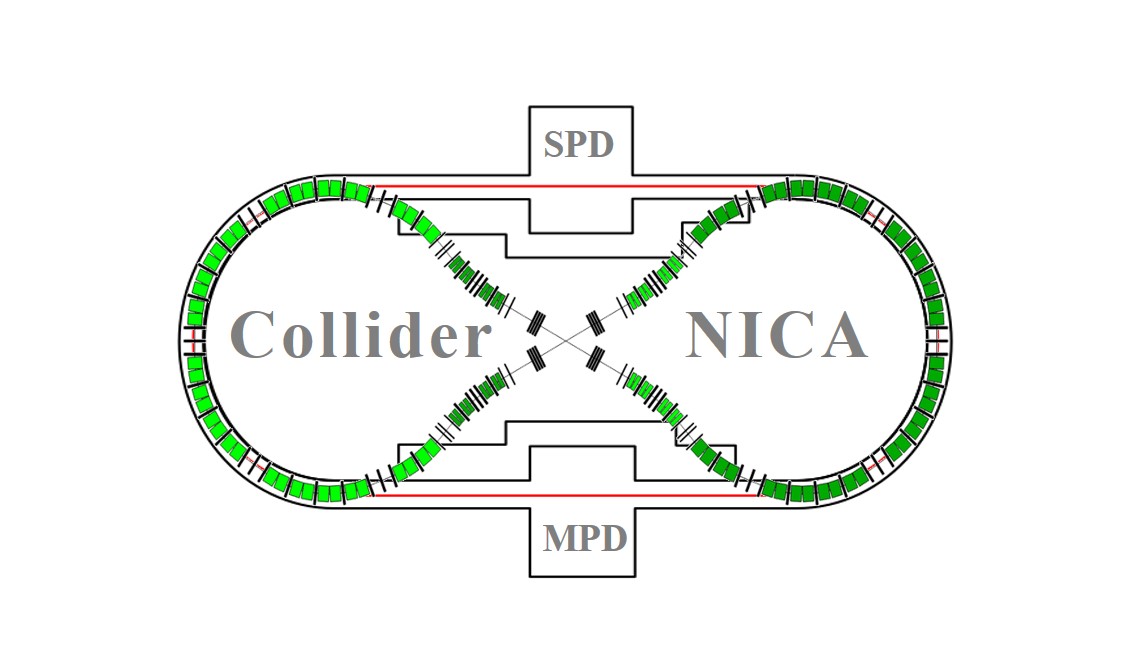
The paper considers a possibility to use the figure-8 synchrotron as a replacement of the Nuclotron for acceleration of polarized proton and deuteron beams at the NICA accelerator complex. The synchrotron arcs are placed inside the NICA collider tunnel. The presented design enables preservation of polarization for any ion species (p, d, 3He, etc.) in the entire energy range of the synchrotron. Because of its shape, the ring operates in the spin transparency mode. The direction of polarization is controlled by a spin navigator which uses weak solenoidal fields. The synchrotron can also be used as a storage ring for high precision experiments with polarized beams beyond its use as an injector to the collider. The results of numerical simulations of spin dynamics for acceleration of protons and deuterons are presented.
For the reconstruction problem, the universal representation of inverse Radon transforms implies the needed complexity of the direct Radon transforms which leads to additional contributions. In the standard theory of generalized functions, if the outset (origin) function which generates the Radon image is a pure-real function, as a rule, the complexity of Radon transforms becomes in question. In the paper, we discuss the Fourier slice theorem analyzing the degenerated (singular) points as possible sources of the complexity. We also demonstrate different methods to generate the needed complexity at the intermediate stage of calculations. Besides, we show that the introduction of the hybrid (Wigner-like) function ensures naturally the corresponding complexity. The discussed complexity not only provides the additional contribution to the inverse Radon transforms, but also makes an essential impact on the reconstruction and optimization procedures within the framework of the incorrect problems. The presented methods can be effectively used for the practical tasks of reconstruction problems.
Issue 4 (Volume 2) 2025
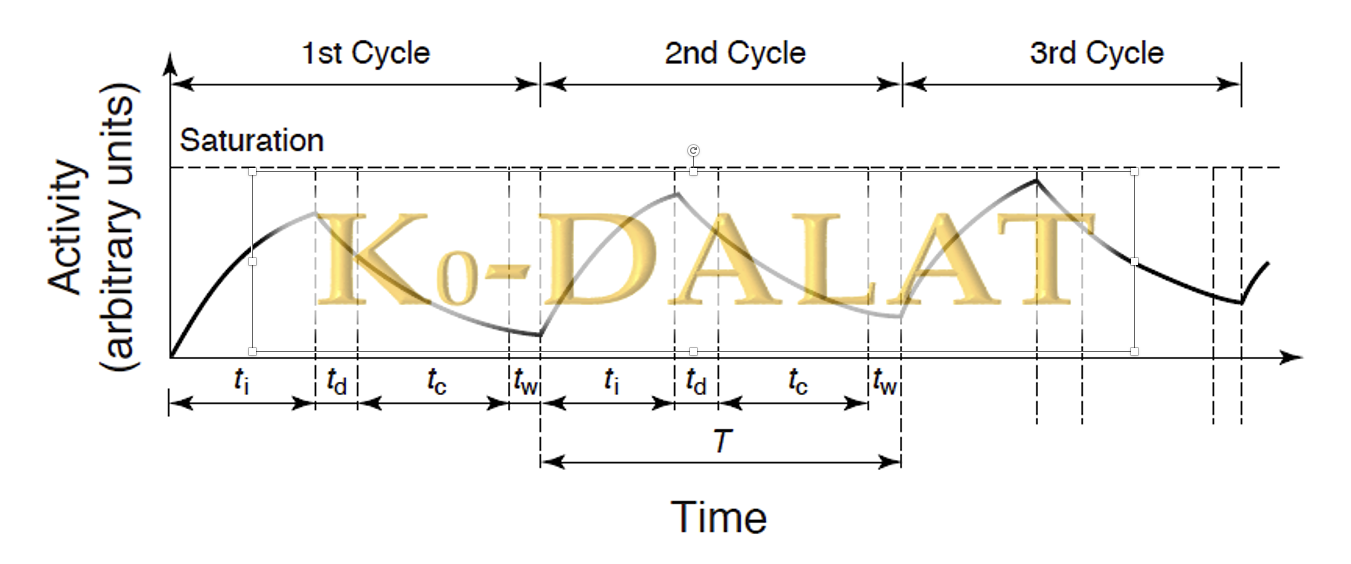
An optimized k0-standardized neutron activation analysis method incorporating cyclic irradiations (k0-CNAA) for short-lived radionuclides (SLRNs) has been developed at the Dalat research reactor. This paper highlights precise reactor parameter characterization using a cyclic irradiation system, simple sample preparation, and advanced calibration of HPGe detector-based gamma-ray spectrometry for SLRNs’ rapid multielement determination. By targeting SLRNs such as 77mSe, 110Ag, 20F, 179mHf, 52V, and 46mSc, with half-lives from seconds to minutes, the method enables quantification of elements essential for biological and environmental research. The in-house developed “k0-Dalat” software, featuring high automation, supports complete analysis. Method accuracy was validated using certified reference materials (SMELS-I, NIST-SRM-1566b, NIST-SRM-2711a), achieving deviations under 8% from certified values. Detection limits ranged from 0.1 to 1.9 mg/kg for target elements in biological samples, confirming the method’s high sensitivity and suitability for similar matrices.
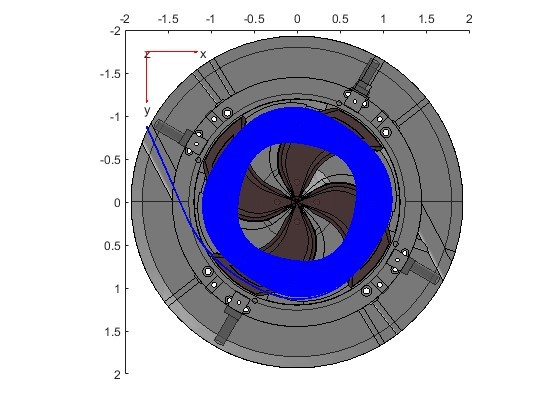
With the emergence of the FLASH irradiation method in proton therapy, the need for high-current accelerators has grown significantly. Addressing this demand, the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) has initiated the development of the MSC230, a compact isochronous cyclotron designed to produce high-intensity proton beams at 230 MeV for advanced biomedical research. Currently, the technical design of the cyclotron is in progress at D. V. Efremov Institute of Electrophysical Apparatus. Modifications during this phase often necessitate additional calculations, resulting in updates to the magnetic field configuration and beam dynamics. This article details the design methodologies and computational tools employed in the MSC230 project.
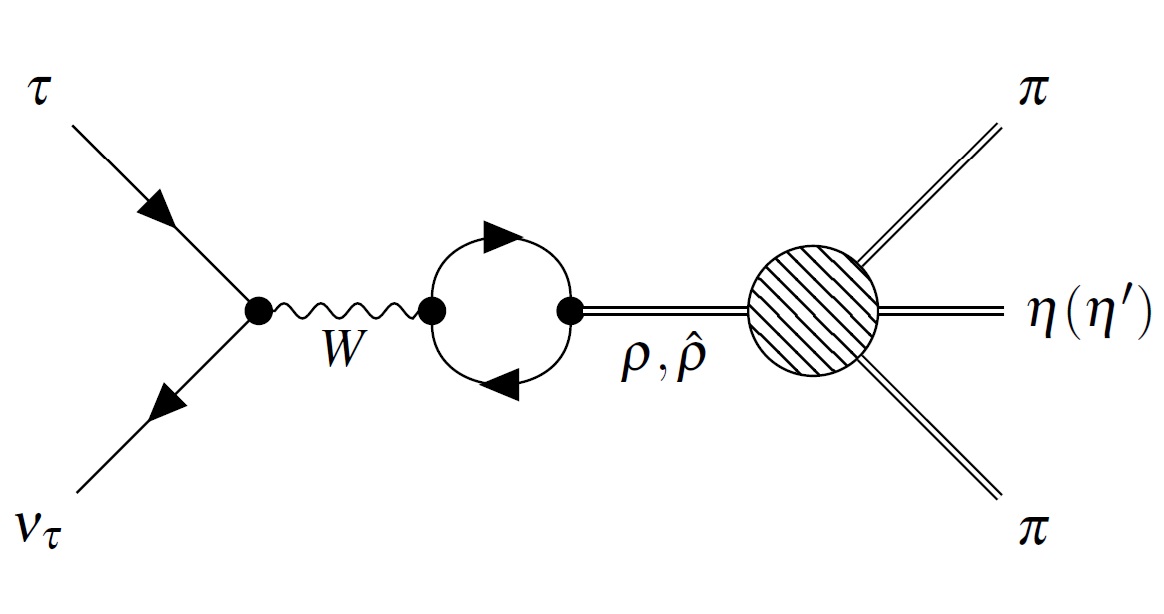
In the framework of the extended Nambu–Jona-Lasinio model, the processes τ → ππη(η′)ντ and τ → πηη(η′)ντ are considered taking into account mesons in the ground and first radially excited intermediate states. It is shown that in the processes τ → ππη(η′)ντ the vector channel is dominant, and in the processes τ → πηη(η′)ντ the main contribution is given by the axial-vector channel. The scalar meson a0 plays a dominant role in processes with two η mesons in the final state. The significance of the relative phase between the ground and first radially excited states for these processes is shown. The obtained results for the τ → ππηντ process are in satisfactory agreement with the recent experimental data from BaBar and CMD-3, which differ from the averaged values given in the PDG tables.
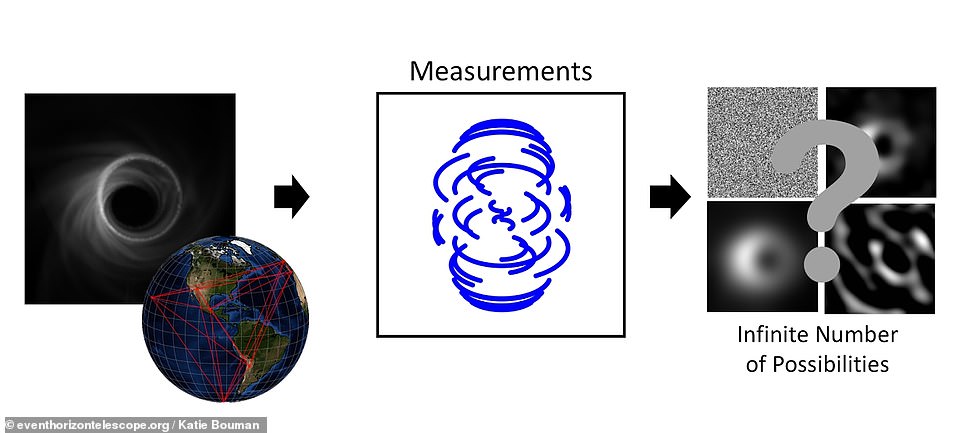
General Relativity (GR) was created in November 1915, and since its creation this theory has undergone many tests. The first realistic cosmological models were proposed in the works of Friedmann, written in the 1920s. For a long time, Friedmann’s cosmological works were actually banned in the Soviet Union due to philosophical reasons, since the models where the birth and evolution of the Universe occurs were considered ideologically unacceptable. Due to great achievements in relativity and cosmology and due to increasing interest in these branches of science in the last decades, we recall the development of relativistic astrophysics and contribution of Russian researchers to these studies. Since one of the world leaders in physical cosmology A. A. Friedmann passed away in September 1925, it is reasonable to outline the main achievements of physical cosmology over the past 100 years. We also discuss observational and theoretical achievements in confirmations of relativistic observational predictions for black holes, including the closest supermassive black hole in our Galactic Center. We outline the evolution of black hole shadow from the purely theoretical concept to observable quantities for supermassive black holes in Sgr A* and M87*.
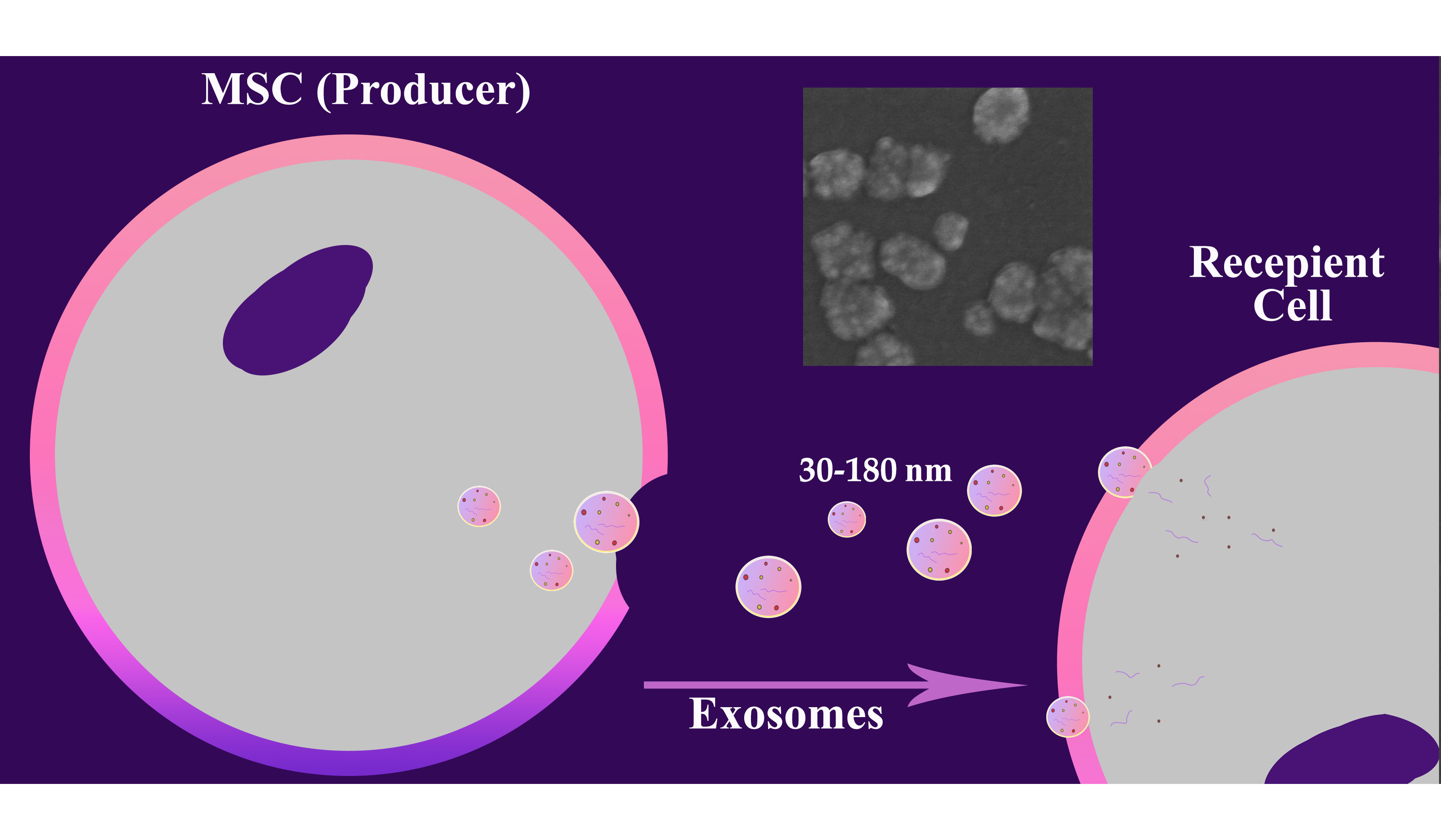
This study provides a comparative analysis of various components of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) conditioned media (CM) obtained using serum-containing and serum-free culture methods, revealing significant differences in their composition and potential clinical applicability. Serum-containing CM exhibits significantly higher levels of total protein, non-vesicular RNA, exosomes, and nanoparticles compared to serum-free CM, reflecting the contribution of both the MSC secretome and residual fetal bovine serum components. Ultrafiltration-based fractionation (0.2 µm–50 kDa) allows the isolation of fraction enriched in exosomes and proteins, preserving the functionally significant components of the MSC secretome. This strategy effectively captures small vesicles and mid-sized proteins while excluding larger or smaller biomolecules, enhancing utility for targeted analyses. The presented data underscore the need for context-driven CM selection and provide information for choosing the optimal strategy for obtaining the MSC secretome balancing yield, purity, and regulatory demands in MSC research and therapy.